A must-have when choosing a water pump! Basic knowledge makes you an expert
Water pump refers to a machine that transfers liquid energy through mechanical energy, and can be used to transport water, oil, acid-base liquid, emulsion, suspended lotion, liquid metal, etc.
Water pumps can be divided into blade pumps, positive displacement pumps, and fluid power pumps according to their working principles.
According to the medium being transported, it can be divided into clean water pumps, oil pumps, mud pumps, sewage pumps, acid pumps, alkali pumps, etc.
According to the prime mover, it can be divided into electric pumps, pneumatic (steam) pumps, magnetic pumps, hydraulic pumps, manual pumps, etc.
The main performance parameters of a water pump include flow rate, head, power, and voltage. Head is the main operational performance parameter of a water pump, which refers to the height at which the pump can lift water waves.
The cavitation of a water pump is caused by the vaporization of water. After cavitation occurs, the metal surface will be damaged under the pressure of water hammer.
1、 Water pump
A water pump is a mechanical device that transports or pressurizes liquids. It transfers the mechanical energy or other external energy of the prime mover to the liquid, increasing the energy of the liquid. It is mainly used to transport liquids including water, oil, acid-base liquids, emulsions, suspensions, and liquid metals.
2、 Classification of water pumps
In the petroleum and chemical industries, the amount, properties, and pressure of liquids that need to be transported vary. In order to meet the requirements of these different situations, various types of water pumps have been designed and manufactured, resulting in different classification methods for water pumps.
(1) Classified by working principle:
① Vane pump: This is a mechanical device that relies on the high-speed rotating impeller inside the pump to transfer energy to the liquid for liquid transportation. There are various forms of pumps belonging to this type, including centrifugal pumps, mixed flow pumps, axial flow pumps, and vortex pumps.
② Positive displacement pump: It uses the periodic variation of the volume of the pump chamber (pump casing or cylinder) to transport liquid, and its discharge process is intermittent. This type of pump, also known as a positive displacement pump, can be divided into two types: reciprocating pump and rotary pump.
③ Fluid power pump: It relies on the energy of another working fluid to pump or press liquids, that is, to transport liquids by relying on the static pressure or kinetic energy of the fluid.
(2) Classified by the medium being transported:
According to the medium being transported, it can be divided into clean water pumps, oil pumps, mud pumps, sewage pumps, acid pumps, alkali pumps, etc.
(3) Classified by prime mover:
According to the prime mover, it can be divided into electric pumps, pneumatic (steam) pumps, magnetic pumps, hydraulic pumps, manual pumps, etc.
3、 Working performance parameters
① Flow rate: Unit: cubic meters per second (m) ³/ h) Instantaneous flow refers to the amount of fluid flowing through the effective cross-section of a closed pipeline or open channel per unit time, also known as instantaneous flow rate. The volume of fluid flowing through a certain section of a pipeline per unit time is called the volumetric flow rate of that cross-section. Abbreviated as traffic, represented by Q.
② Head: The unit is meters (M), and head refers to the height at which a water pump can lift water. It is an important performance parameter of a water pump, also known as pressure head. Represented by H.
③ Power: The unit is kilowatt hours (KW), and power refers to the amount of work done by an object in a unit of time. That is, power is a physical quantity that describes the speed of work done. The amount of work is fixed, and the shorter the time, the greater the power value. Represented by the letter N.
④ Voltage: The unit is volts (V), also known as potential difference or potential difference, which is a physical quantity that measures the energy difference generated by a unit charge in an electrostatic field due to different potentials.
Common voltage: 220V; 380V; 660V; 1140V. Represented by the letter V.
⑤ Electric control cabinet: also known as control cabinet, divided into three categories: self coupling step-down start; Soft start; Variable frequency start.
4、 Calculation of head
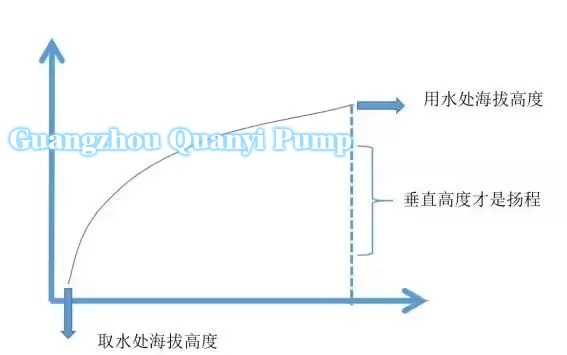
Calculation diagram of water pump head:
Head=vertical height at the water intake+pipeline loss (1 km of horizontal travel with a head of 20 meters; loss of 0.8 meters for 45 ° elbows and 1.5 meters for 90 ° elbows)+outlet pressure
① Vertical height: abbreviated as vertical height, refers to the vertical height difference between the center point of the water pump outlet and the center point of the pipeline end. If the height difference is large, such as exceeding 100 meters, it can be considered as the height difference from the horizontal plane to the end of the pipeline, ignoring the suction lift of three to five meters.
② Pipeline loss, abbreviated as pipeline loss, refers to the energy loss caused by the flow of liquid in the pipeline, including friction loss and accessory loss (such as valve elbow).
③ Outlet pressure: refers to the water pressure at the end of the pipeline.
5、 Calculation of water pump power

6、 Cavitation margin
When a water pump is working, the liquid at the inlet of the impeller will generate vapor under a certain vacuum pressure. The vaporized bubbles will cause erosion on the metal surface of the impeller under the impact of liquid particles, thereby damaging the impeller and other metals. At this time, the vacuum pressure is called vaporization pressure, and the cavitation margin refers to the excess energy per unit weight of liquid at the pump inlet that exceeds the vaporization pressure. Units are indicated in meters and expressed in (NPSH) r.
7、 Cavitation phenomenon
The cavitation of a water pump is caused by the vaporization of water, which is the process of water transforming from liquid to vapor.
The vaporization of water is related to temperature and pressure to a certain extent. At a certain pressure, water only begins to vaporize when the temperature reaches a certain value.
If the pressure drops to a certain value at a certain temperature, water will also vaporize, and this pressure is called the vaporization pressure of water at that temperature.
If during the flow process, the pressure in a certain local area is equal to or lower than the vaporization pressure corresponding to the water temperature, water will vaporize at that location.
When vaporization occurs, many small bubbles of steam mixed with gas are formed.
When bubbles flow with water from the low-pressure area to the high-pressure area, the bubbles rupture under the action of high-pressure, and high-pressure water flows at a high speed towards the space occupied by these original bubbles, forming an impact force.
The metal surface will be severely damaged under water hammer pressure. Therefore, the process of bubble formation, development, rupture, and even material damage is called cavitation phenomenon.
